Preprint Published on "A Novel Data Integration Method Using Contextual Graph Embeddings."
2025-11-13
- article
We have released a new preprint about "Contextual Graph Embeddings for Heterogeneous Data Integration" on arXiv.
This study proposes a novel embedding method that combines structural information (graphs) with contextual information (language models) to address challenges in schema matching and entity resolution—two core tasks in integrating heterogeneous data sources. These tasks are often hindered by differences in structure, inconsistencies in labeling, and variations in data representation across datasets.
In heterogeneous data integration, issues such as inconsistent column names, mismatched schema structures, and high rates of missing values create significant barriers and require substantial manual effort. Traditional rule-based or knowledge-based methods tend to be domain-dependent and struggle to capture the complex structural properties of diverse datasets. Graph neural networks (GNNs) can model multi-hop relationships, but they require a large amount of labeled data and extensive tuning, making them less practical for real-world applications.
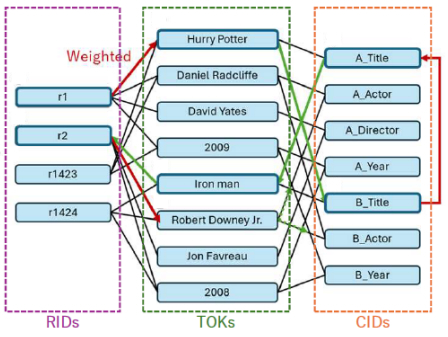
To address these limitations, we introduce a new approach—Contextual Graph Embedding—designed specifically for heterogeneous data integration. Our method constructs a four-partite graph connecting rows (RIDs), columns (CIDs), and cell values (tokens), while incorporating column names, descriptions, and statistical characteristics. During embedding learning, we perform weighted random walks based on column importance and similarity, enabling the model to capture both structural and contextual cues rather than relying solely on token co-occurrence.
We conducted systematic experiments using datasets that reflect common real-world properties, including variations in data size, missing rate, domain specificity, and column/row overlap rates. The results show that our method consistently outperforms existing approaches under diverse conditions, particularly in challenging scenarios involving high missingness or predominantly numerical attributes—areas where traditional methods often struggle. At the same time, the study also identifies remaining challenges, such as cases in which semantically different columns share similar names and are mistakenly matched.
This research not only proposes a new integration method that unifies structural and contextual information, but also quantitatively evaluates how dataset characteristics influence matching performance—an aspect that has received limited attention in prior work. As future directions, we aim to refine similarity metrics and design semi-automated workflows with domain experts, with the goal of enabling more efficient and reliable data integration in practical settings.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.09001
Title: Contextual Graph Embeddings: Accounting for Data Characteristics in Heterogeneous Data Integration
Authors: Yuka Haruki, Shigeru Ishikura, Kazuya Demachi, Teruaki Hayashi
Abstract: As organizations continue to access diverse datasets, the demand for effective data integration has increased. Key tasks in this process, such as schema matching and entity resolution, are essential but often require significant effort. Although previous studies have aimed to automate these tasks, the influence of dataset characteristics on the matching effectiveness has not been thoroughly examined, and combinations of different methods remain limited. This study introduces a contextual graph embedding technique that integrates structural details from tabular data and contextual elements such as column descriptions and external knowledge. Tests conducted on datasets with varying properties such as domain specificity, data size, missing rate, and overlap rate showed that our approach consistently surpassed existing graph-based methods, especially in difficult scenarios such those with a high proportion of numerical values or significant missing data. However, we identified specific failure cases, such as columns that were semantically similar but distinct, which remains a challenge for our method. The study highlights two main insights: (i) contextual embeddings enhance the matching reliability, and (ii) dataset characteristics significantly affect the integration outcomes. These contributions can advance the development of practical data integration systems that can support real-world enterprise applications.