「LLMを用いたマルチエージェントデータ市場シミュレーション」に関するプレプリントを公開しました。
2025-11-19
- article
「LLMを用いたマルチエージェントデータ市場シミュレーション」に関するプレプリントをarxivに公開しました。
データ流通の高度化に伴い、第三者からデータを購入・交換するデータ市場(data marketplace)がイノベーションの源泉として注目されています。しかし、実際の市場では、買い手・売り手がどのような目的を持ち、どのように戦略的に行動するのか、その結果として市場全体がどのように変化していくのかについて、体系的な理解は十分ではありません。本研究は、これらの課題に対し、大規模言語モデル(LLM)を活用した新しいマルチエージェント・シミュレーションを提案しました。
これまでのデータ市場シミュレーションは、ルールベース型やエージェントの行動をあらかじめ条件化するモデルベースが主流でした。しかし、これらの手法は、エージェントの行動が固定的であるため「多様な目的」「状況に応じた戦略の変更」「市場トレンドへの適応」など、実際のデータ市場に見られる複雑な意思決定の再現が困難であるという問題がありました。
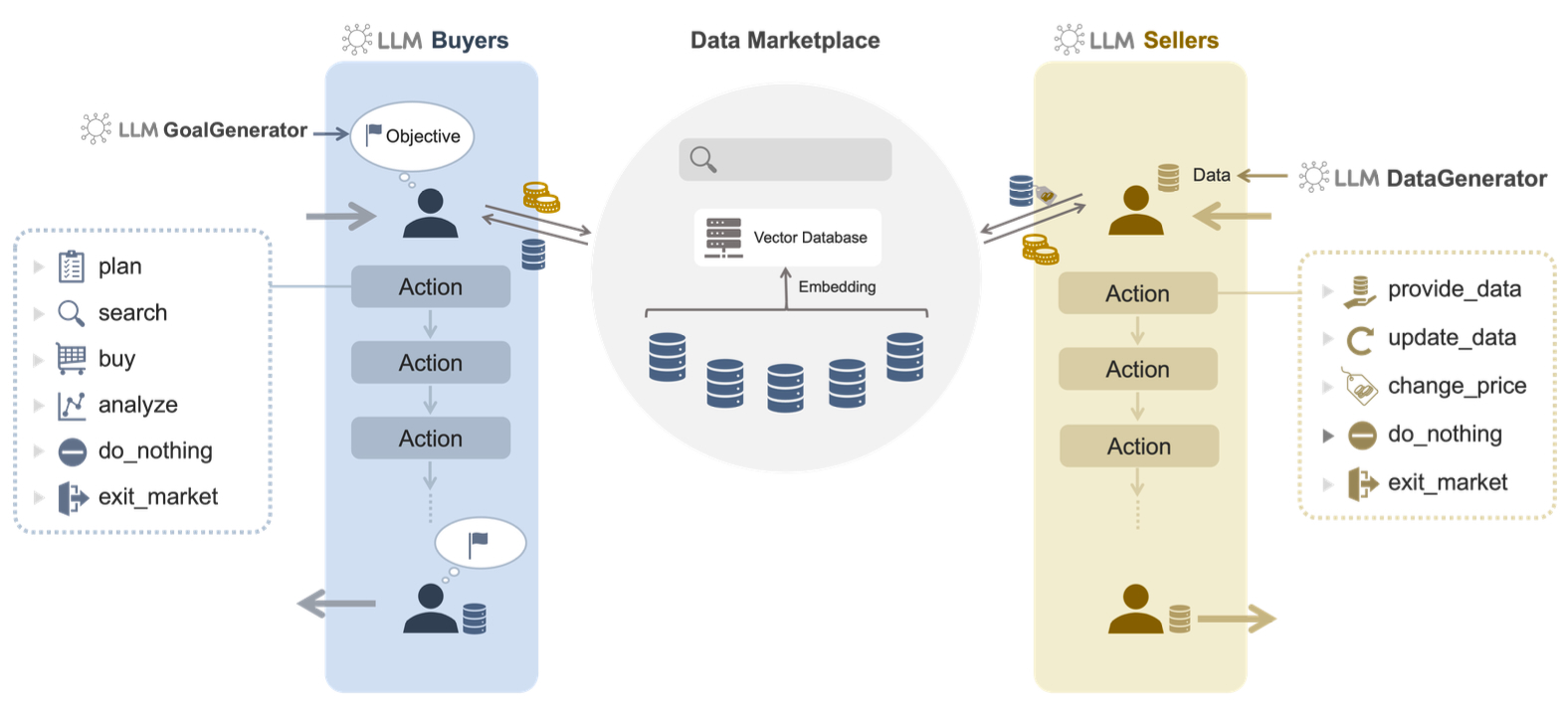
本研究では、買い手・売り手エージェントそれぞれに自然言語で記述された“目的”を与え、LLMによる推論を通じてデータ探索・購買・価格設定・更新などの行動を自律的に選択できるシステムを構築しました。この仕組みにより、従来のルールベース型モデルでは表現が難しかった複雑な行動を再現することが可能になりました。
シミュレーションでは、データセットごとの取引回数や買い手ごとの購買行動、同一データの繰り返し購入といった市場構造の特徴を分析し、実際のデータ市場サービスの取引データと比較しました。その結果、特定データの人気集中、買い手・売り手ネットワークのスケールフリー構造、分野別トレンドの出現といった市場の特徴を高い精度で再現できることが明らかになりました。特に、時間経過とともに特定分野への需要集中が生じる様子も観測されました。これは、現実の市場でも見られる重要な現象の一つです。
本研究は、戦略性と目的意識を備えたエージェントが相互に作用することで市場全体の構造とダイナミクスを明らかにし、これからのデータ市場の制度設計のためのシミュレータ開発を目指しています。今後は、異種データ形式の統合や、購入後の詳細な分析行動のモデル化、複数エージェント間の情報共有・協調も含め、より高度なデータ市場の理解と設計支援に向けて拡張していきます。
https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.13233
タイトル:LLM-based Multi-Agent System for Simulating Strategic and Goal-Oriented Data Marketplaces
著者:Jun Sashihara, Yukihisa Fujita, Kota Nakamura, Masahiro Kuwahara, Teruaki Hayashi
アブストラクト:Data marketplaces, which mediate the purchase and exchange of data from third parties, have attracted growing attention for reducing the cost and effort of data collection while enabling the trading of diverse datasets. However, a systematic understanding of the interactions between market participants, data, and regulations remains limited. To address this gap, we propose a Large Language Model-based Multi-Agent System (LLM-MAS) for data marketplaces. In our framework, buyer and seller agents powered by LLMs operate with explicit objectives and autonomously perform strategic actions, such as planning, searching, purchasing, pricing, and updating data. These agents can reason about market dynamics, forecast future demand, and adjust strategies accordingly. Unlike conventional model-based simulations, which are typically constrained to predefined rules, LLM-MAS supports broader and more adaptive behavior selection through natural language reasoning. We evaluated the framework via simulation experiments using three distribution-based metrics: (1) the number of purchases per dataset, (2) the number of purchases per buyer, and (3) the number of repeated purchases of the same dataset. The results demonstrate that LLM-MAS more faithfully reproduces trading patterns observed in real data marketplaces compared to traditional approaches, and further captures the emergence and evolution of market trends.