「信頼性の高い大規模言語モデルの説明可能性」に関する論文のプレプリントを公開しました。
2025-11-06
- article
「信頼性の高い説明を生成するための大規模言語モデルの説明可能性」に関する論文のプレプリントをarxivに公開しました。
本研究では、近年注目を集める大規模言語モデル(LLM: Large Language Model)の説明可能性(Explainability)に焦点を当て、その信頼性と有効性を高めるための理論的・実証的枠組みを提案しました。
生成AIが医療や自動運転などの社会基盤にも応用される中、「なぜこの出力をしたのか」を理解し、利用者がその判断を信頼できるようにすることが急務です。しかし、LLMはその内部構造が複雑で、出力の根拠が不透明になりやすいという課題があります。
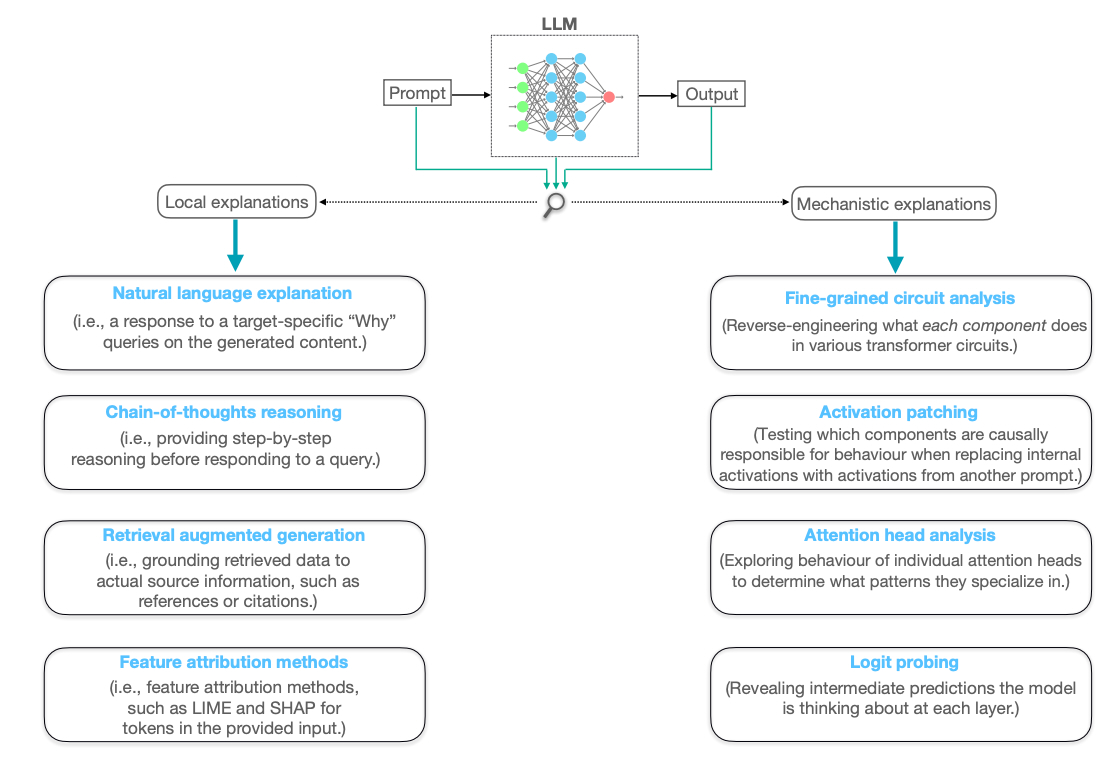
そこで本研究では、局所的な出力理由を明らかにする「ローカルな説明可能性(local explainability)」と、モデル内部の動作原理を解析する「機構的解釈可能性(mechanistic interpretability)」という二つの観点から、LLMの説明生成と信頼形成のあり方を体系的に整理しました。
さらに、医療診断支援や自動運転といった高リスク領域を対象に、説明が利用者の理解と信頼に与える影響を分析し、説明の忠実性や明示性が信頼形成に重要であることを論じました。
本研究は、AIシステムの透明性と説明責任を高めるための方法論を提供するとともに、説明可能なAI(XAI)の実装に向けた新たな方向性を提示するものになります。今後は、モデル構造の可視化技術や説明評価の標準化を進め、社会的に信頼されるAIの実現に貢献していくことが期待されます。
本研究は早矢仕講師がVisiting Professorとしてカナダのアルバータ大学に滞在していた際のXAI Labのメンバーとの研究の一部です。ぜひご一読ください。
https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.17256
タイトル:Explainability of Large Language Models: Opportunities and Challenges toward Generating Trustworthy Explanations
著者:Shahin Atakishiyev, Housam K.B. Babiker, Jiayi Dai, Nawshad Farruque, Teruaki Hayashi, Nafisa Sadaf Hriti, Md Abed Rahman, Iain Smith, Mi-Young Kim, Osmar R. Zaïane, Randy Goebel
アブストラクト:Large language models have exhibited impressive performance across a broad range of downstream tasks in natural language processing. However, how a language model predicts the next token and generates content is not generally understandable by humans. Furthermore, these models often make errors in prediction and reasoning, known as hallucinations. These errors underscore the urgent need to better understand and interpret the intricate inner workings of language models and how they generate predictive outputs. Motivated by this gap, this paper investigates local explainability and mechanistic interpretability within Transformer-based large language models to foster trust in such models. In this regard, our paper aims to make three key contributions. First, we present a review of local explainability and mechanistic interpretability approaches and insights from relevant studies in the literature. Furthermore, we describe experimental studies on explainability and reasoning with large language models in two critical domains -- healthcare and autonomous driving -- and analyze the trust implications of such explanations for explanation receivers. Finally, we summarize current unaddressed issues in the evolving landscape of LLM explainability and outline the opportunities, critical challenges, and future directions toward generating human-aligned, trustworthy LLM explanations.